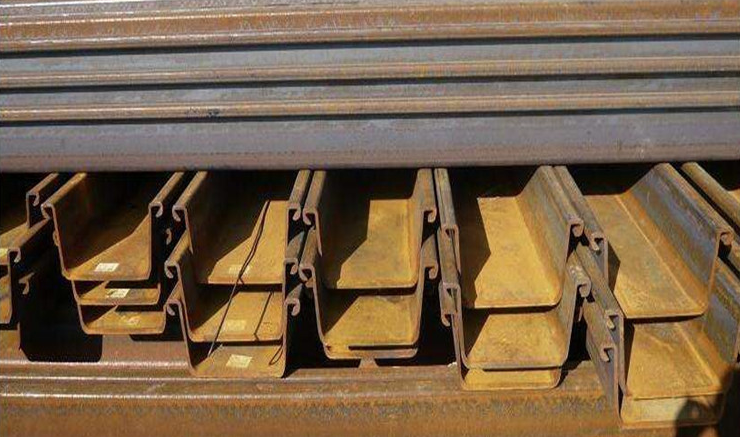
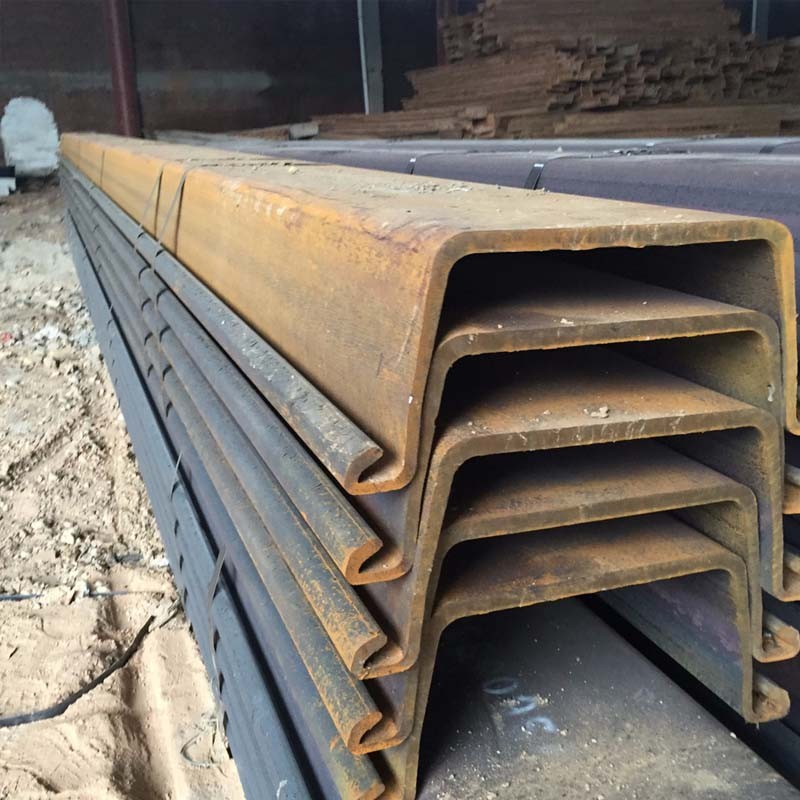
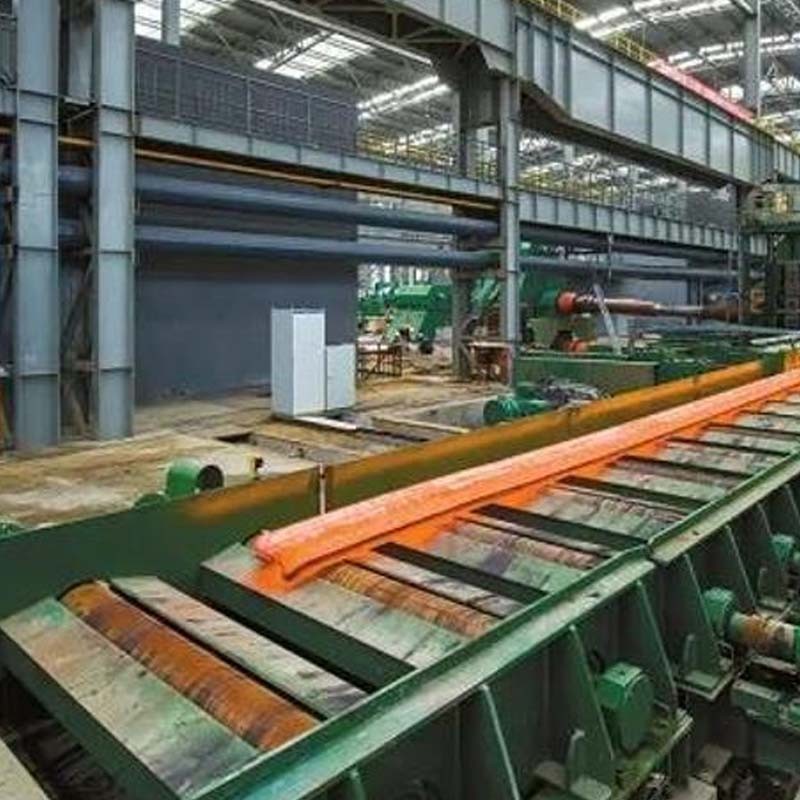
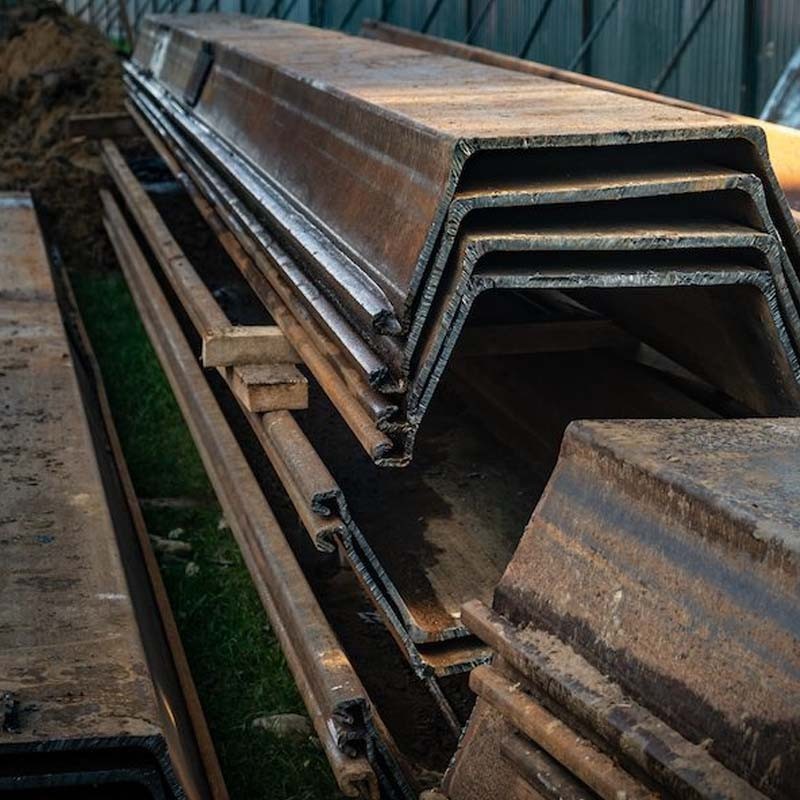
Steel sheet piles are a type of construction material used in various engineering and construction projects, particularly for creating retaining walls and cofferdams. They are designed to provide lateral support to soil or water, preventing erosion, and stabilizing excavations.
Key features of steel sheet piles include:
Interlocking Sections:
Steel sheet piles have interlocking edges or joints, which enable them to be driven into the ground and linked together to form continuous walls or barriers.
Versatility:
They are used in a wide range of applications, such as constructing cofferdams, retaining walls, bulkheads, flood protection systems, and foundations for various structures.
Strength and Durability:
Steel sheet piles offer high strength, allowing them to withstand heavy loads and forces, making them suitable for both temporary and permanent structures.
Water Resistance:
As they are commonly used in waterfront applications, they are designed to resist the corrosive effects of water and offer long-term reliability.
Recyclability:
Steel sheet piles are environmentally friendly since they are made from recyclable materials and can be reused in other projects.
Hot-Rolled and Cold-Formed:
There are two main types of steel sheet piles: hot-rolled and cold-formed. Hot-rolled sheet piles are produced by rolling steel at high temperatures, making them well-suited for heavy-duty applications. Cold-formed sheet piles are manufactured by bending steel plates at room temperature, making them more cost-effective for lighter-duty projects.
Steel sheet piles have significantly contributed to the advancement of civil engineering, enabling the construction of various infrastructure projects around the world. Their adaptability, strength, and cost-effectiveness make them a preferred choice for many construction and marine engineering applications.
Application of steel sheet pile:
Steel sheet piles are widely used. In permanent structures, they can be used in wharfs, unloading yards, embankments, retaining walls, retaining walls, breakwaters, diversion dikes, docks, gates, etc.; in temporary structures, they can be used It can be used for retaining soil, water, sand, etc. for mountain closure, temporary bank expansion, flow interruption, bridge cofferdam, large pipeline laying and temporary ditch excavation; in flood fighting and emergency rescue, it can be used for flood control, subsidence prevention, and quicksand prevention.
In China, the standards for steel sheet piles are primarily established and maintained by the Chinese National Standards (GB/T) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (MOHURD). These standards ensure the quality, performance, and safety of steel sheet piles used in various construction and engineering applications.
The most relevant Chinese National Standards related to steel sheet piles include:
GB/T 20933-2021: Cold-formed steel sheet piles. This standard specifies the technical requirements for cold-formed steel sheet piles used in construction projects.
GB/T 20935: Hot-rolled steel sheet piles. This standard specifies the technical requirements for hot-rolled steel sheet piles used in construction projects.
GB 50018: Code for Design of Steel Structures. This code provides guidance on the design of various steel structures, including steel sheet pile retaining walls and other piling applications.
GB 50205: Code for Construction and Acceptance of Steel Sheet Pile Structures. This code provides guidelines for the construction and acceptance of steel sheet pile structures, ensuring proper installation and compliance with standards.
These standards cover various aspects, including material specifications, manufacturing processes, dimensions, tolerances, and design considerations for steel sheet piles in China.
In the United States, the standards for steel sheet piles are primarily established and maintained by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). These organizations set the specifications and guidelines for various types of steel sheet piles used in construction and engineering applications.
ASTM standards related to steel sheet piles include:
ASTM A328 / A328M: Standard Specification for Steel Sheet Piling. This specification covers carbon steel sheet piling used in the construction of cofferdams, excavation shoring, and other applications.
ASTM A572 / A572M: Standard Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy Columbium-Vanadium Structural Steel. While not specific to sheet piles, this specification covers the standard requirements for high-strength low-alloy structural steel, which can be applicable to certain types of steel sheet piles.
AASHTO standards are often used for transportation-related projects and may include specifications for steel sheet piles in specific applications. For instance:
AASHTO M270: Standard Specification for Structural Steel for Bridges. Similar to ASTM A572, this specification covers various grades of structural steel used in bridge construction, which may be relevant when considering steel sheet piles for bridge abutments or other bridge-related applications.
In the United Kingdom, the standards for steel sheet piles are mainly governed by the British Standards Institution (BSI) and Eurocodes. These standards ensure the quality, performance, and safety of steel sheet piles used in various construction and engineering applications.
The most relevant BSI and Eurocode standards related to steel sheet piles include:
BS EN 10248: Hot-rolled sheet piling of non-alloy steels - Part 1: Technical delivery conditions. This standard specifies the requirements for hot-rolled non-alloy steel sheet piling used for construction purposes.
BS EN 1993-5: Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 5: Piling. This Eurocode provides guidance on the design of steel structures, including steel sheet pile retaining walls and other piling applications.
BS 5950-1: Structural use of steelwork in building - Part 1: Code of practice for design - Rolled and welded sections. While not specific to sheet piles, this standard outlines the design requirements for various steel structures, which can be applicable to steel sheet pile designs.
BS 5950-5: Structural use of steelwork in building - Part 5: Code of practice for design of cold-formed thin gauge sections. Similar to BS 5950-1, this standard focuses on the design of cold-formed thin gauge steel sections, which may be relevant to certain types of steel sheet piles.
In Japan, the standards for steel sheet piles are primarily established and maintained by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS). The JIS sets specifications for various industrial products to ensure their quality, safety, and reliability.
The most relevant JIS standards related to steel sheet piles include:
JIS A 5523: Steel Pipe Piles. This standard covers steel pipe piles used for foundation construction, including steel sheet pile walls.
JIS A 5528: Hot Rolled Steel Sheet Piles. This standard specifies the technical requirements for hot-rolled steel sheet piles used in construction projects.
JIS A 5530: Steel Sheet Piles. This standard covers the general aspects of steel sheet piles, including dimensions, tolerances, material properties, and sectional properties.
JIS A 5372: Cold Formed Steel Sheet Piles. This standard specifies the technical requirements for cold-formed steel sheet piles used in construction applications.
These JIS standards ensure that steel sheet piles used in Japan meet specific performance criteria, and they cover various aspects, such as dimensions, material properties, and manufacturing processes.
Japanese construction and engineering professionals typically refer to these JIS standards when selecting and using steel sheet piles for different projects, including building foundations, waterfront structures, and other geotechnical applications.
Sheet pile allowable deviation value:
Height allowable deviation ±3MM
Absolute deviation of width +10MM ~ 5MM
The bending deflection can be smoothly passed through the entire length using a 2M long locking sample, and the deflection is less than 1%.
The plane of the pile end should be flat and the inclination should be less than 3MM.

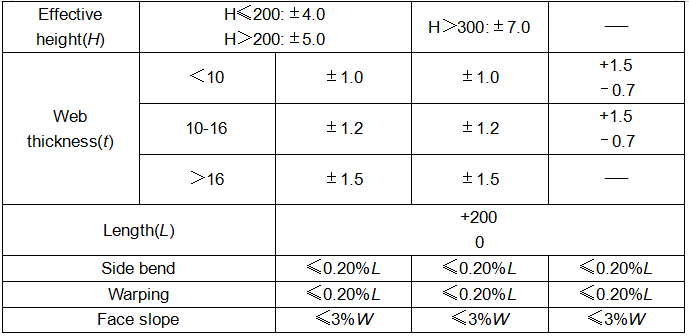
Weight and tolerance
The steel sheet pile should be delivered according to the theoretical weight (theoretical weight is calculated according to the density of 7.85 g/cm3). It can also be delivered according to the actual weight after negotiation between the supplier and the buyer and specified in the contract.
The allowable deviation between the actual weight of the delivery and the theoretical weight should not exceed ±5%.












