Angle steel, also known as angle iron, is a commonly used building material, steel with an L-shaped cross-section. It is made of steel plate or flat steel after a series of processing, and its shape is equilateral angle. Angle steel is widely used in various building components due to its advantages of high strength, strong corrosion resistance, easy processing, and easy splicing.
One of the main advantages of angle steel is its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. The L-shaped design distributes load evenly along its length, making it highly resistant to bending and deflection. Angle steel is commonly used as structural members in the construction of buildings, bridges, towers and various types of infrastructure.
Angles are available in different sizes including different leg lengths and thicknesses to suit various applications and load requirements. The name of the angle usually includes the length of each leg in millimeters and the thickness of the steel in millimeters. For example, an angle named "L50x50x5" has a dimension of 50 mm per leg and a thickness of 5 mm.
Angle steel has the following characteristics:
1. High strength: Since the section of the angle steel is L-shaped, it has high bending strength and bearing capacity.
2. Good plasticity: Angle steel is easy to process, and can be processed by cutting, bending, drilling and other methods.
3. Good anti-corrosion performance: The surface of angle steel is usually treated with hot-dip galvanizing, which can improve its anti-rust performance and prolong its service life.
4. Moderate price: The price of angle steel is relatively low, which is suitable for mass purchase and use.
The use of angle steel
1. Construction field: Angle steel can be used for supports, frames, beams, columns, corners and other parts in building structures.
2. Mechanical field: Angle steel can be used as the connector of machine parts, such as assembled frame, machine bed, etc.
3. Electric power field: Angle steel can be used for suspension and support of power towers, transmission lines, etc.
4. Transportation field: Angle steel can be used for support and reinforcement in the construction of railways, highways, bridges, etc.
5. Petrochemical field: Angle steel can be used for support and fixation of petrochemical equipment and pipeline support.
Overall, angle steel is a versatile and versatile structural steel that is valued for its strength, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. It plays a key role in supporting various structures and is a fundamental component of modern architectural and engineering practice.
In China, the standards for angle steel, along with other structural steel sections, are established by the Chinese National Standards (GB) or the Chinese National Building Codes (GB/T). The most commonly used standard for angle steel is GB/T 706.
GB/T 706-2016 specifies the dimensions, shapes, weights, and tolerances for hot-rolled equal and unequal angle steel. This standard covers angles with leg lengths ranging from 25 mm to 200 mm and thicknesses from 3 mm to 20 mm.
For hot-rolled equal-leg angles, the legs have the same length, and for hot-rolled unequal-leg angles, one leg is longer than the other. The standard provides dimensional tolerances, allowing for variations in angle steel size within specified limits.
GB/T 706-2016 also defines the mechanical properties of the angle steel, including yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation, ensuring the quality and performance of the material.
In the United States, the standards for angle steel are governed by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). The most commonly used standard for angle steel is ASTM A36/A36M.
ASTM A36/A36M is a specification that covers carbon structural steel shapes, including angles. It outlines the requirements for hot-rolled and cold-rolled carbon steel bars, plates, and other structural shapes used in general construction and engineering applications.
For angle steel, ASTM A36/A36M specifies the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances. Angle steel manufactured to this standard must have a minimum yield strength of 36,000 psi (or 250 MPa) and a minimum tensile strength of 58,000-80,000 psi (or 400-550 MPa).
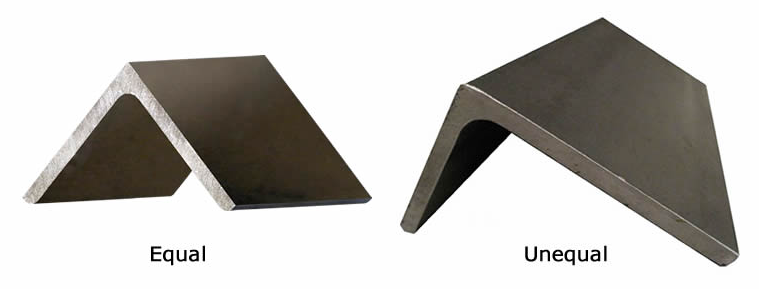
Angles are classified as equal-leg angles and unequal-leg angles. Equal-leg angles have both legs of the same length, while unequal-leg angles have one leg shorter than the other.
The designation of angle steel typically includes the dimensions of the legs (in inches) and the thickness of the steel (in inches). For example, an equal-leg angle with the designation "L3 x 3 x 1/4" would have legs measuring 3 inches each and a thickness of 1/4 inch.
ASTM A36 is a widely used material specification for angle steel and various other structural steel shapes due to its excellent weldability, machinability, and cost-effectiveness. It is one of the most commonly used standards for angle steel in construction and general structural applications in the United States.
In the United Kingdom, the standards for angle steel, along with other structural steel sections, are established by the British Standards Institution (BSI). The most commonly used standard for angle steel is BS EN 10056-1:2017.
BS EN 10056-1:2017 specifies the dimensions, tolerances, and general requirements for hot-rolled equal and unequal steel angles. This standard covers angles with leg lengths ranging from 20 mm to 200 mm and thicknesses from 3 mm to 20 mm.
For hot-rolled equal-leg angles, the legs have the same length, and for hot-rolled unequal-leg angles, one leg is longer than the other. The standard provides dimensional tolerances, allowing for variations in angle steel size within specified limits.
In addition to specifying the dimensions, BS EN 10056-1:2017 also defines the mechanical properties of the angle steel, including yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation.
In Japan, the standards for angle steel, like other structural steel sections, are established by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS). The most commonly used standard for angle steel is JIS G 3192.
JIS G 3192 specifies the dimensions, sectional properties, and technical requirements for hot-rolled steel sections, including angles. This standard covers angles with leg lengths ranging from 25 mm to 200 mm and thicknesses from 3 mm to 15 mm.
For hot-rolled equal-leg angles, the legs have the same length, and for hot-rolled unequal-leg angles, one leg is longer than the other. The standard provides dimensional tolerances, allowing for variations in angle steel size within specified limits.
JIS G 3192 also defines the mechanical properties of the angle steel, including yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation, ensuring the quality and performance of the material.












