

A steel grade is a numbering system used to identify different types and properties of steel. Every country or region has its steel grade system, and these grades are usually A steel grade is a numbering system used to identify different types and properties of steel. Every country or region has its steel grade system, and these grades are usually composed of numbers, letters, and symbols, which could describe the composition, properties, uses, and other information of steel. For example, China's steel grade system is GB/T; the USA's steel grade system is ASTM or SAE; the European Union's steel grade system is EN/DIN EN, and so on.
The significance of these steel grade systems is that they provide a uniform standard that enables a quick understanding of the properties and uses of steel. By understanding steel grades, engineers, manufacturers, and users can select the correct steel for their needs, ensuring it has the performance and reliability required for a particular application. Grades also facilitate communication, ensuring consistency and quality control in the steel supply chain. Grade systems may vary from country to country and region to region, so it is critical to understand the correspondence of the different systems in international trade and cooperation.
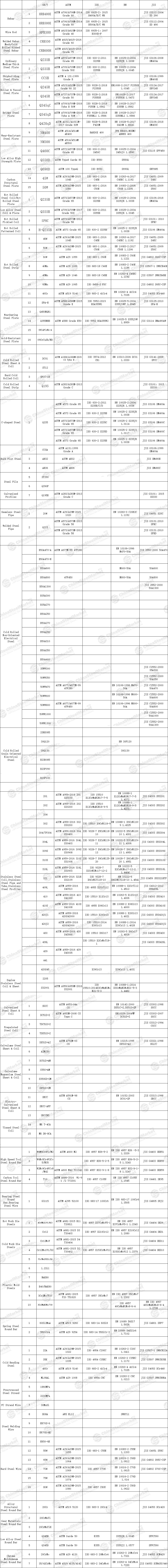
In this feature article, I will provide readers with a brief introduction to the steel grade system of the following countries. At the end of the article, I will offer a cross-reference table of all the steel products our company is responsible for for the reference of all customers. Meanwhile, we also welcome professionals from all walks of life to give us positive feedback.
1. Chinese Steel Grades
There are two methods of expressing steel grades in China, which are "Notations for designation of iron and steel" (GB/T 221-2008) and "Unified numbering system for designation of iron, steel and alloy" (GB/T 17616-2013). In the work, we combine these two ways to use. That is to say, a steel model has two forms of grades and numerical designations, which are related to each other.
In practical application, "Notations for designation of iron and steel" (GB/T 221-2008) is more common. Each steel product has its coding rules, usually combined with hanyu pinyin letters, chemical element symbols, and Arabic numerals. For example, Q in the Q235 refers to the yield strength, which means the minimum yield strength of 235N/mm2 carbon steel. There are other letters to be added at the end of the grade to explain, such as Q345R, R refers to the pressure vessel. It means the minimum yield strength of 345N/mm2 boiler and pressure vessel carbon steel.
The different types of steel grade representations covered on this website are as follows:
(1) Carbon structural steel and low alloy structural steel grade is usually composed of four parts: the first part is the prefix symbol + strength value (MPa), such as Q indicates the yield strength of steel; the second part of the English letters indicate the quality of the steel grade; the third part of the deoxidation mode of the representation of symbols, the use of the English letters; the fourth part of the use of suffixes to indicate the product's application, characteristics and process methods. But these four parts are not necessarily labeled at the same time.
(2) The high-quality carbon structural steel grade usually has five parts. The first part of the two Arabic numerals indicates the average carbon content (mass fraction, calculated in parts per million); the second part of the steel with the highest element of the chemical element symbols; the third part of the English letters indicates the metallurgical quality of steel, for example, with the A that the high-quality steel; the fourth, the fifth part of the deoxidation method and product use, characteristics and other content. Spring steel grades are in the same way as this product.
(3) The grade of alloy structural steel consists of four parts. The first part is two Arabic numerals indicate the average carbon content (mass fraction); the second part of the chemical element symbols and Arabic numerals show the alloying elements and their content; the third and fourth part of the metallurgical quality of steel and product use, characteristics and other content. High-speed tool steel grades in the same way.
(4) The cold-heading steel grade has three parts. The first part is the symbol ML for cold heading steel; the second part indicates the carbon content in Arabic numerals; the third part is the same as the second for alloy structural steel.
(5) Stainless steel grades include the chemical element symbols of steel composition and the content of each element in two parts.
(6) Bearing steel grade consists of two parts: the first part is G, which means bearing steel; the second is the chemical symbols of alloying elements and their content. The rest of the representation is the same as alloy structural steel.
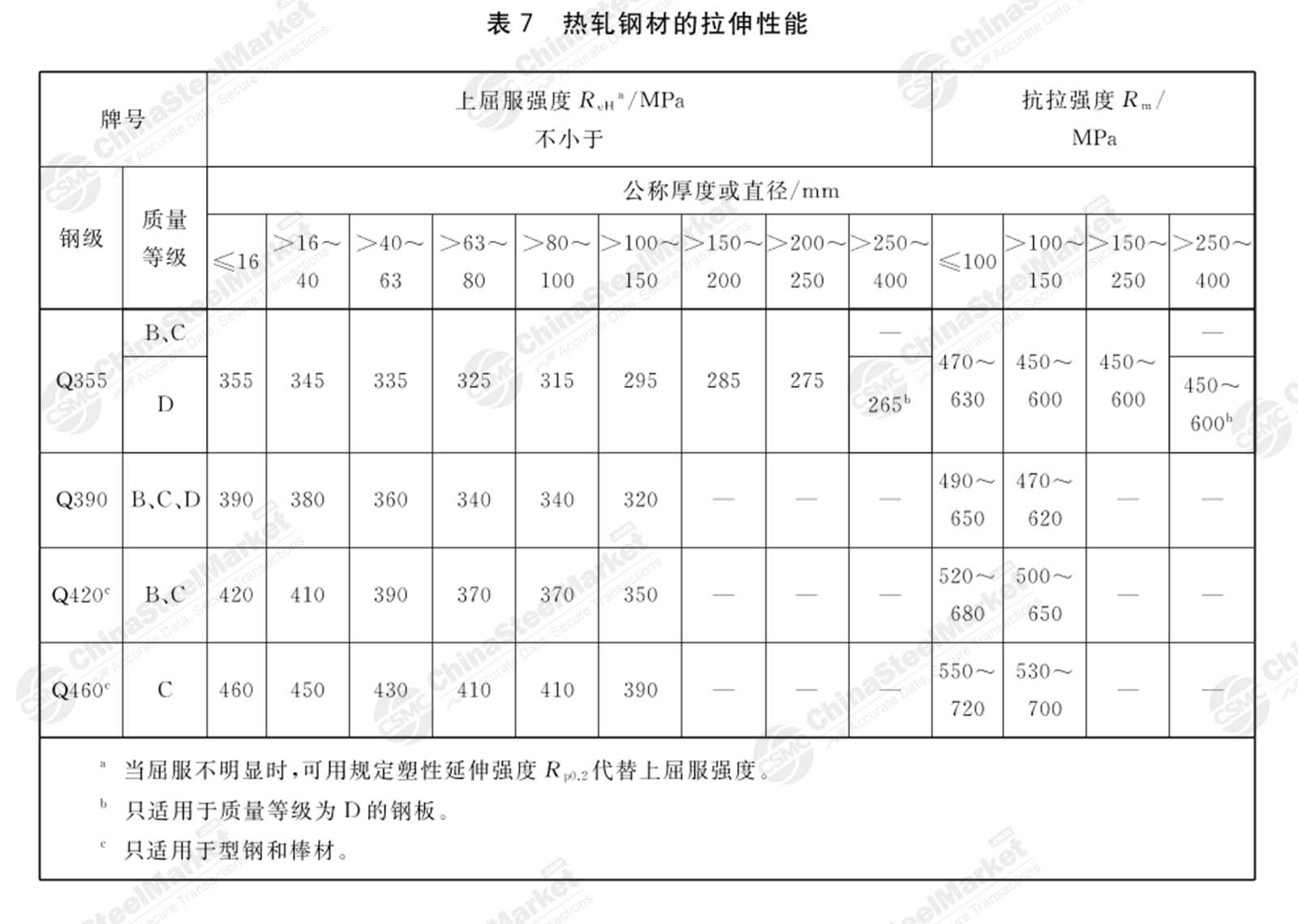
Hot Rolled Series Steel Grades
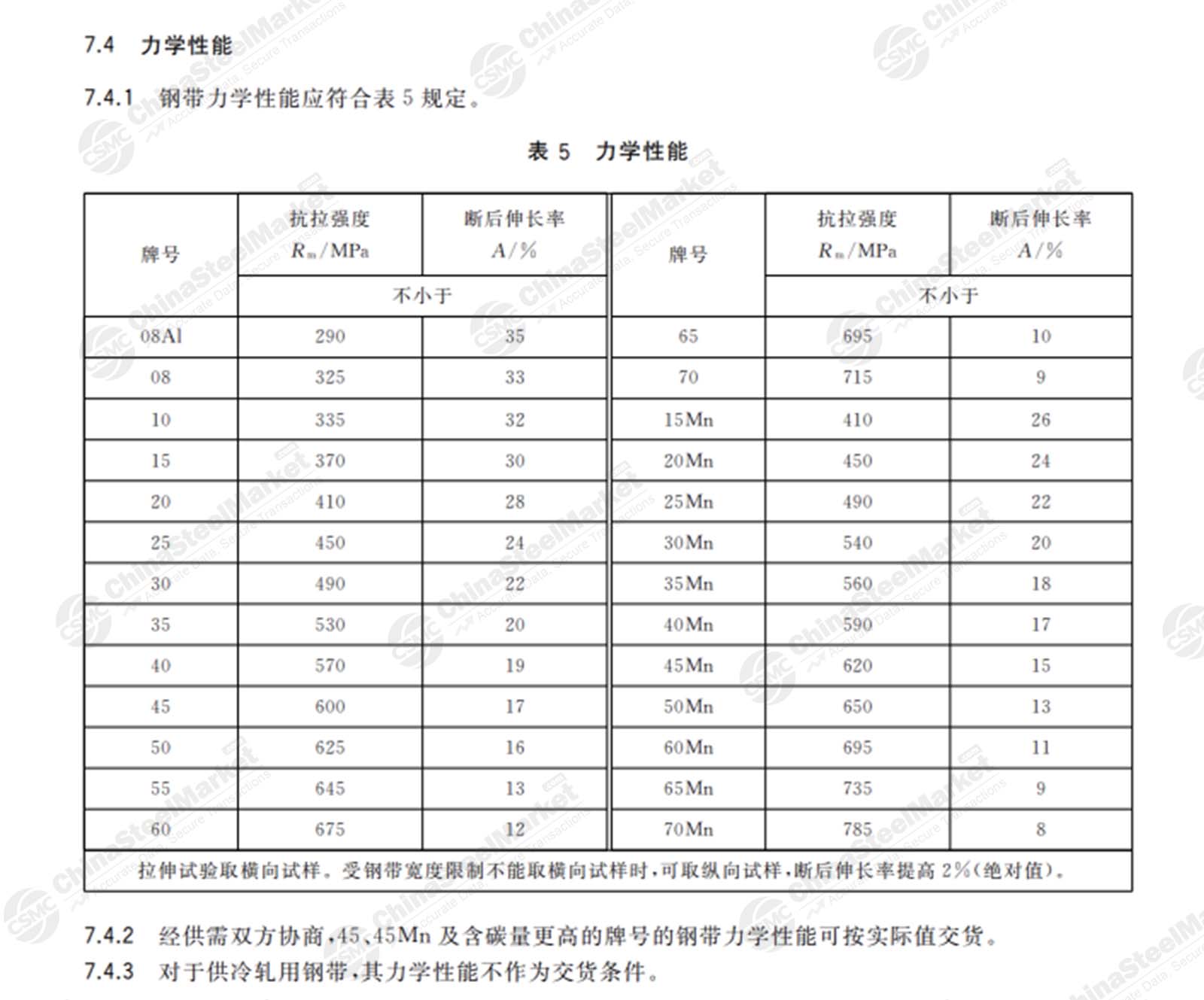
High-Quality Carbon Structural Steel Grades
1. USA Steel Grades
Many societies and associations engage in customizing steel standards in the United States. We work primarily with ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards as a benchmark.
For the ASTM grade system, structural steels are similar to the SAE system, including four digits. The first two numbers indicate the type of steel, and the last two show the average content of carbon in the steel. For example, 1015 represents a carbon structural steel with an average mass fraction of carbon of 0.15%. Stainless steel and heat-resistant steel grades in the ASTM standardized system are composed of three digits, with the first number indicating the types of steel and the second and third digits showing the serial number. For example, 3xx means the nickel-chromium austenitic steel. Tool steel grades are composed of a letter indicating the type of steel and a sequential number.
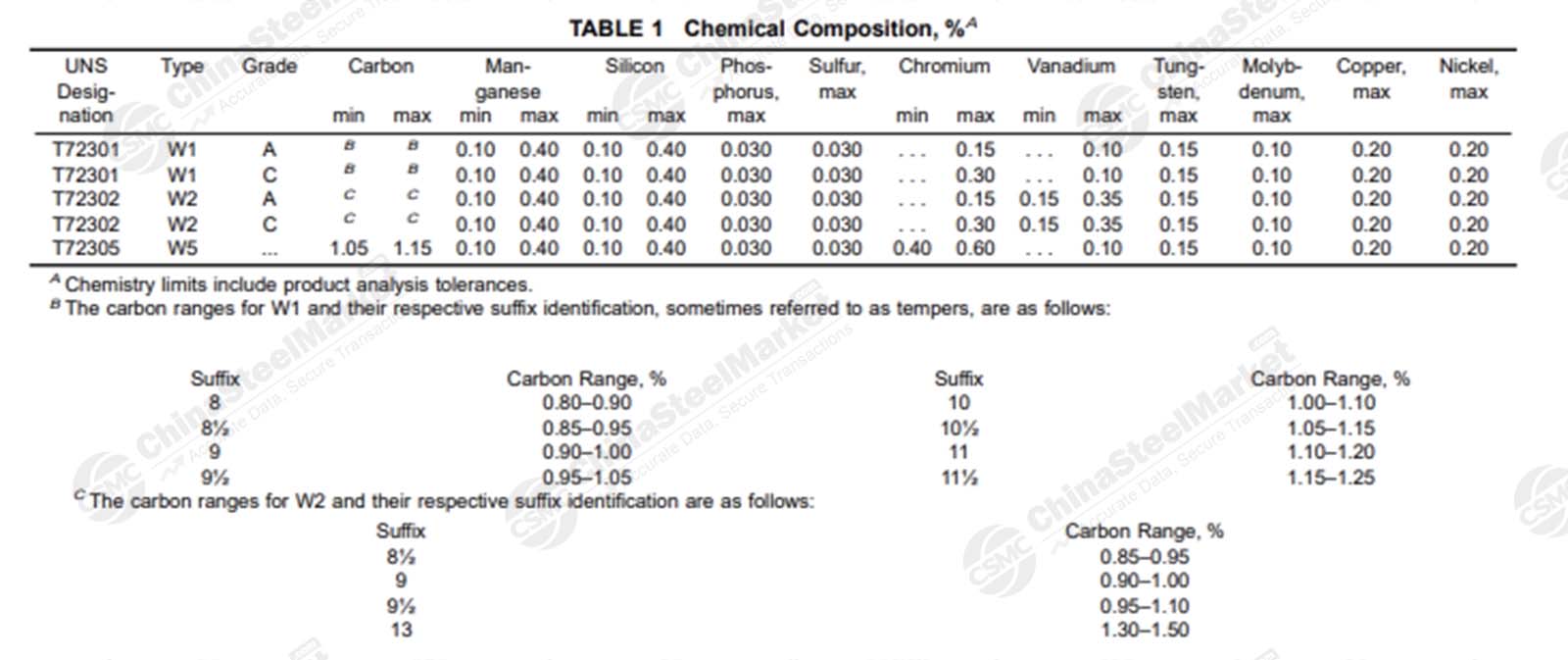
U.S. Carbon Tool Steel Grades
3. ISO Steel Grades
With the ISO international standard system, there are two main methods of representing steel grades. One is the mechanical properties-based representation, including chemical element symbols and performance values; the other is the chemical composition-based representation, including chemical element symbols and composition content values. The former applies to non-alloy steel, low alloy steel, and weathering steel, such as E235 and S235. The latter applies to heat-treated non-alloy steel, stainless steel alloy tool steel, and other steels, such as C45.
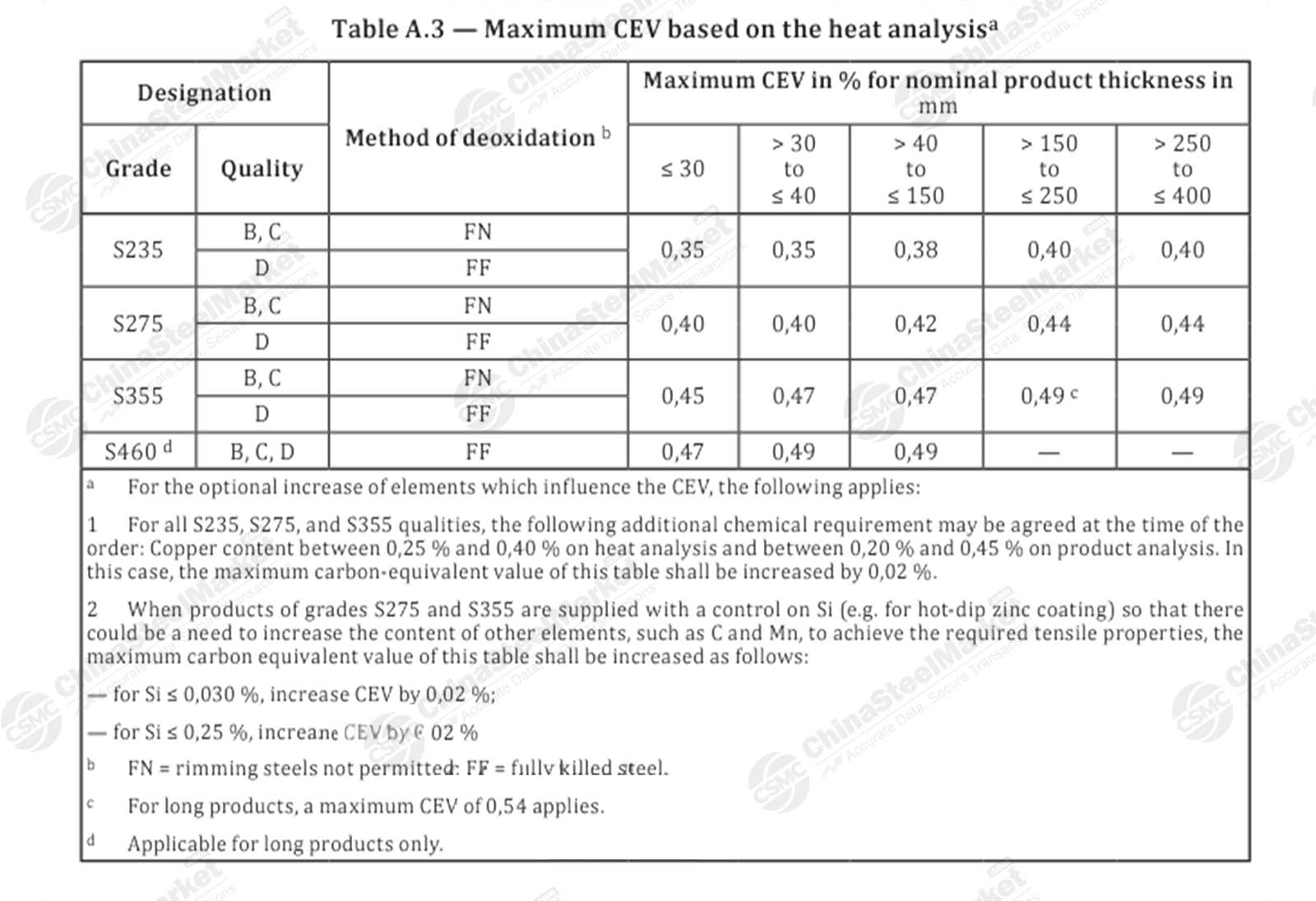
ISO Carbon Structural Steel Grades
4. EN Steel Grades
The steel grade system of the European Union originates from the standards EN (European Standard) and DIN EN (German Industrial Standard - European Standardization). This system often refers to the EN/DIN EN steel grade system. It uses a combination of letters and numbers to identify different types, uses, and properties of steel. These letters and numbers provide significant information about the composition, heat treatment, and mechanical properties. In this system, a typical EN/DIN EN steel grade usually contains the following information: primary use and type identification. A combination of letters and numbers usually indicates the use and type of steel, such as structural steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc.
In the European Union standard system, steel grade mainly includes two kinds of provisions. One is composed of English letters and numbers, applicable to structural steel, pressure vessel steel, and reinforced concrete steel; the other is composed of chemical element symbols and composition content values, applying to alloy steel, stainless steel, and tool steel.
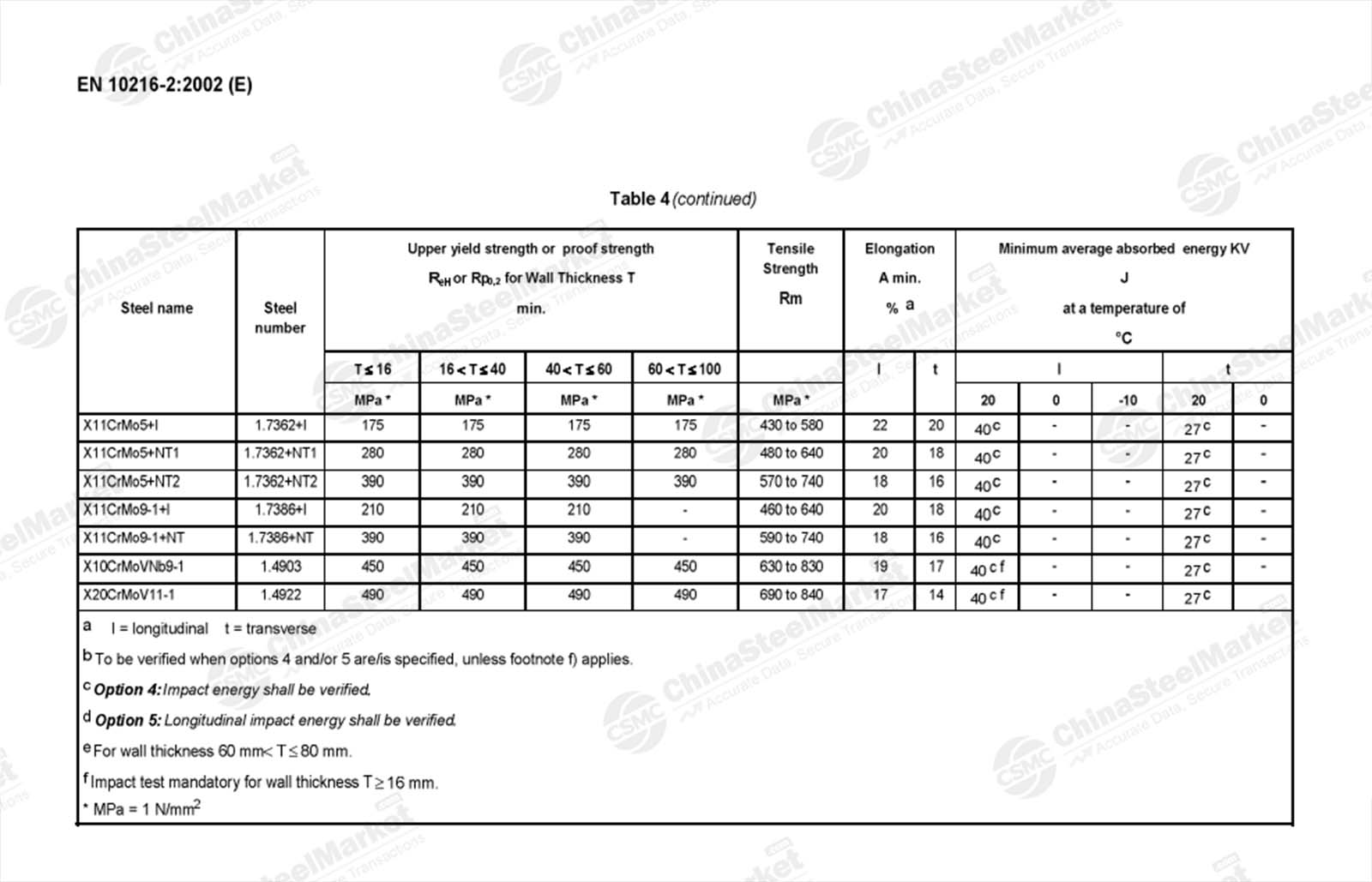
EN Non-Alloyed and Alloyed Steel Seamless Round Tube Grades
5. Japan Steel Grades
The current Japanese steel grade standard is JIS, which is the Japanese Industrial Standard. There is no special provision in the JIS standard. There are only a few common features in the commons.
The grade generally consists of three parts:
The first part is the prefix, such as the letter S for steel and the F for iron.
In the second part, the English letters or the Roman letters of kana pinyin indicate the use of the product, the type of steel, and other contents. For example, SUJ means high-carbon chrome-bearing steel.
The third part with a number indicates the type of steel, steel serial number, or tensile strength (MPa) minimum value. For example, SS400 represents that the minimum tensile strength of carbon structural steel of this kind of material is 400 MPa.
In addition, a suffix letter indicating the shape of the steel, the manufacturing method, the heat treatment, etc., may be added as required.
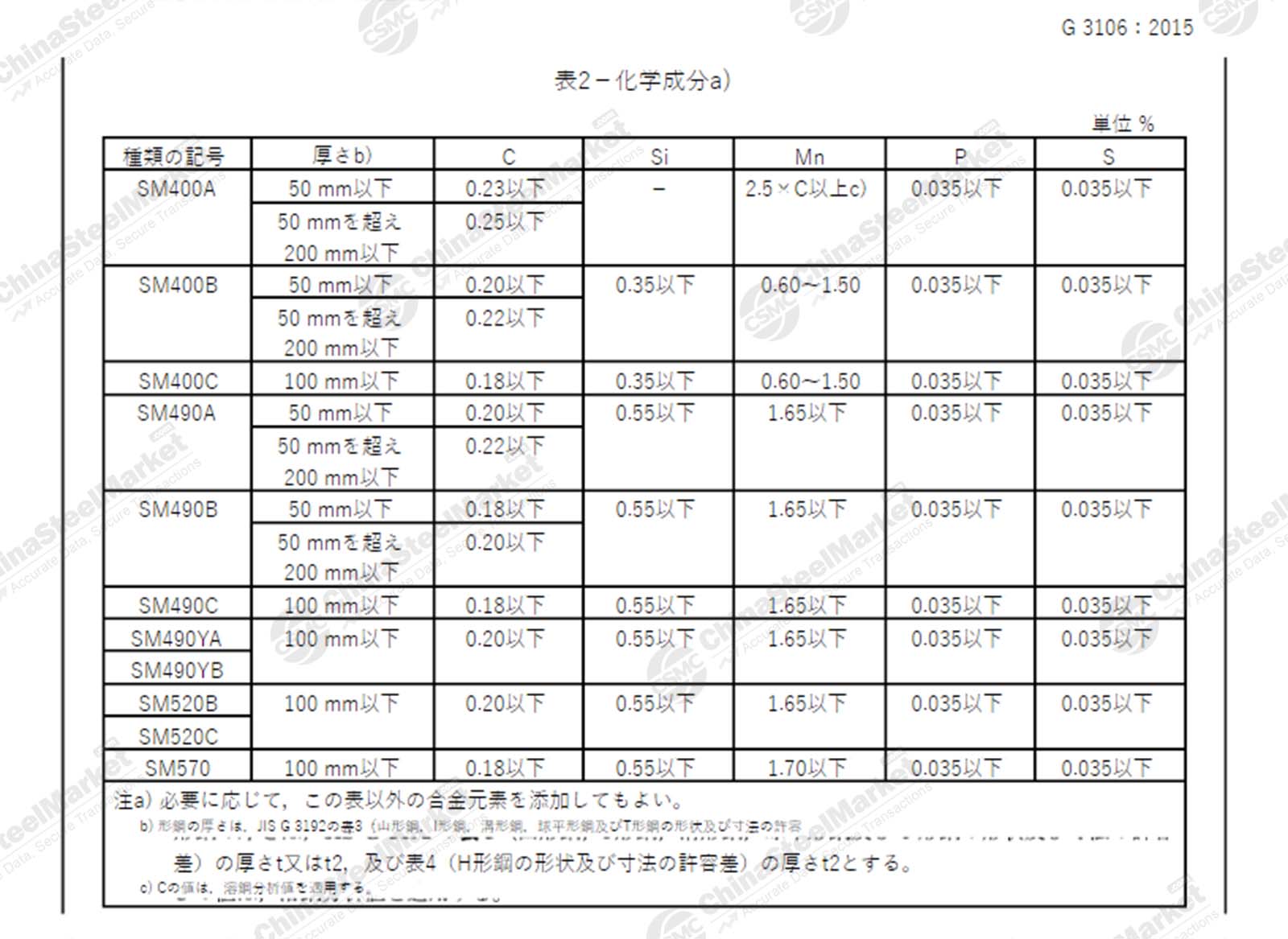
Japan Carbon Structural Steel Grades
The development of national standards for steel grades has a vital impact and significance on the development of steel for the world. First of all, steel is a critical commodity traded globally, and steel trade between different countries and regions needs a set of common standards to ensure the consistency and comparability of materials. With the development of a unified standard for steel grades, international trade can proceed more smoothly, helping to reduce transaction costs and promote cooperation and exchange. Secondly, the performance and use of steel are closely related to its composition and treatment. By setting standards, we can ensure that we can precisely control the quality, performance, and characteristics of all of the steel, thereby reducing the variability in production and improving product consistency and reliability. Thirdly, different grades of steel correspond to their applications and performance requirements. The development of standards-making encourages manufacturers and research institutes to innovate and develop new types of steel that can better meet specific needs. So we can promote the technological advancement and innovation in the industry. Fourth, engineering projects require appropriate materials to ensure project reliability and safety. Standardized steel grades can help engineers select the correct steel for a particular application, thereby improving the design and operational safety of the project. Fifth, different steel grades have differing environmental impacts. Through standardization, the selection of more environmentally friendly steels can be encouraged, helping to reduce resource consumption and environmental impact.
With the increase of global environmental awareness and the development of digital technology, the standard-setting process may become more intelligent and efficient. More attention will be paid to the environmental performance of steel, encouraging the development of more energy-saving and low-carbon emission steel to meet the requirements of global sustainable development. In conclusion, the development of national steel grade standards has a profound impact on the development of the world's steel industry, helping to promote trade, improve quality, promote innovation, and support sustainable development. As technology advances and globalization deepens, standard-setting will continue to adapt to new challenges and needs.
Mail: gianna@chinasteelmarket.com




|

|

|

|

|
| Timely Info | Independent | Platform | Multiple guarantees | Self-operated storage |
| About us | Channel | Useful tools |
|---|---|---|
| About China Steel Market | Prices | Steel Weight Calculation |
| Contact Us | Answers | Why Choose Us |
| Terms & Conditions | Inventory | |
| Privacy Policy | Help |
Hot search words: