

Mold steel is a type of steel used to make molds, such as cold stamping dies, hot forging dies, and die-casting dies. Molds are the main processing tools for manufacturing parts in industrial sectors such as machinery manufacturing, radio instruments, motors, and electrical appliances.
Since the production standards of various countries are different, this has caused certain difficulties for customers in international trade. CSMC will organize and display the Chinese grades and other countries' grades to help customers conduct trade more smoothly.
According to usage, mold steel can be roughly divided into cold-rolled mold steel, hot-rolled mold steel, and plastic mold steel, which are used for forging, stamping, cutting, die-casting, etc.
Ⅰ Cold Work Tool Steel
Cold work tool steels include cold punching dies, wire drawing dies, drawing dies, impression dies, thread rolling dies, thread rolling plates, cold heading dies, and cold extrusion dies. Steel for cold work molds should have high hardness, strength, wear resistance, sufficient toughness, hardenability, hardenability, and other process properties according to the working conditions of the manufactured tools. Alloy tool steel used for such purposes is generally high-carbon alloy steel with a carbon mass fraction of more than 0.80%. Chromium is an important alloying element in this type of steel, and its mass fraction is usually no more than 5%. However, for some mold steels that require very high wear resistance and have very little deformation after quenching, the maximum chromium mass fraction can reach 13%. To form a large amount of carbides, the carbon mass fraction in steel is also very high, up to 2.0%~2.3%. The carbon content of cold work die steel is relatively high, and most of its structures are hypereutectoid steel or ledeburite steel. Commonly used steels include high carbon low alloy steel, high carbon high chromium steel, chromium molybdenum steel, medium carbon chromium tungsten steel, etc.
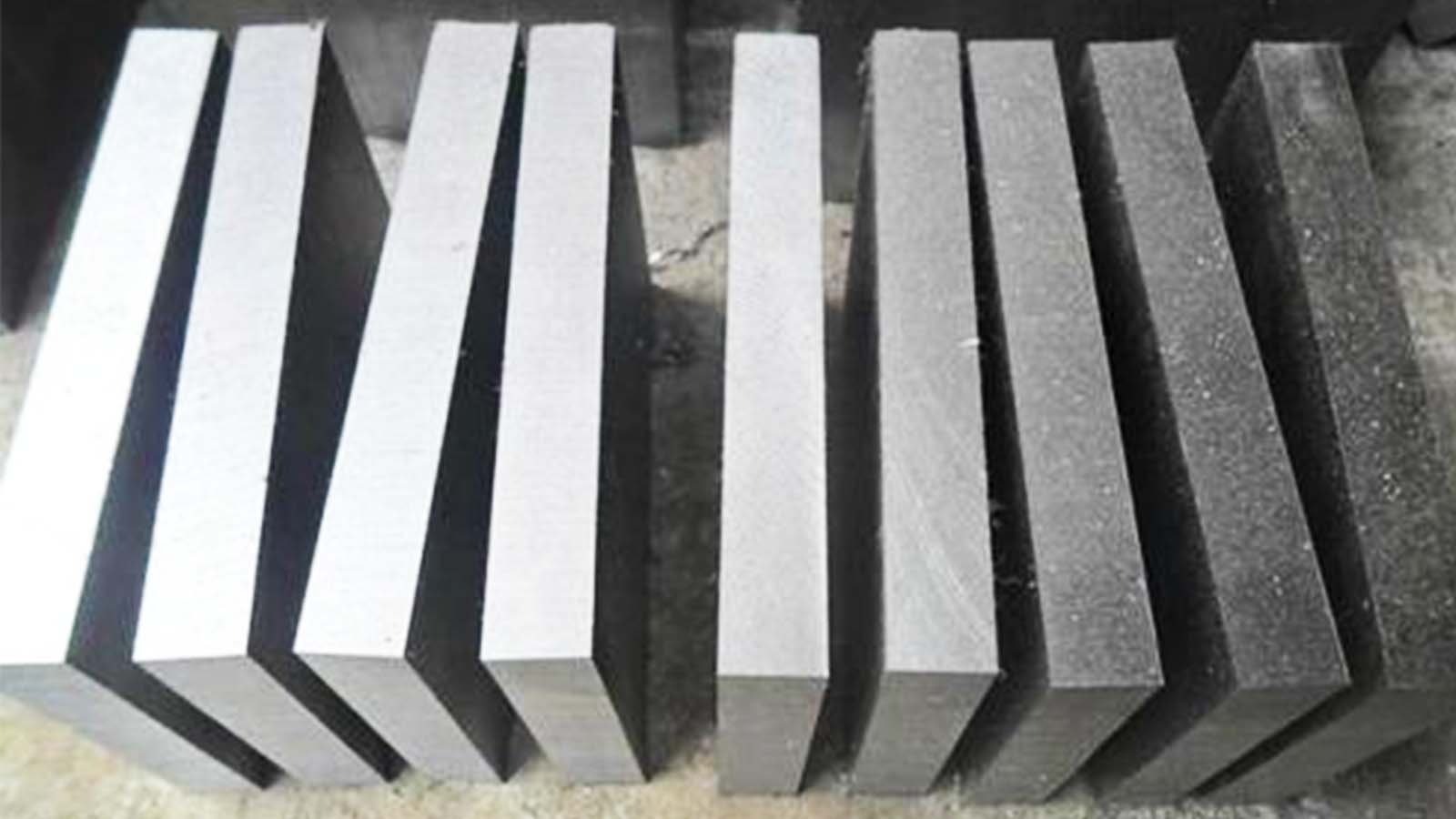

Cold Work Tool Steel
Ⅱ Hot Work Tool Steel
Hot work tool steels are divided into several main types: hammer forging, die forging, extrusion, and die casting, including hot forging dies, press forging dies, stamping dies, hot extrusion dies, and metal die-casting dies. In addition to enduring huge mechanical stress during operation, the thermally deformed mold also has to withstand repeated heating and cooling, causing great thermal stress. In addition to high hardness, strength, red hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, hot work dies steel should also have good high-temperature strength, thermal fatigue stability, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. In addition, hot-rolled mold steel is also required to have high hardenability to ensure consistent mechanical properties across the entire section. For the applications of die-casting molds, it should also have the performance that the surface layer will not produce cracks after being repeatedly heated and cooled. And it can withstand the impact and erosion of liquid metal flow. This type of steel is generally a medium-carbon alloy steel with a carbon mass fraction of 0.30%~0.60%. It is a hypoeutectoid steel. Some steels become eutectoid or eutectoid due to the addition of more alloying elements (such as tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium, etc.). Hypereutectoid steel. Commonly used steels include chromium-manganese steel, chromium-nickel steel, chromium-tungsten steel, etc.

Hot Work Tool Steel
Ⅲ Plastic Mold Steel
Plastic mold steels include thermoplastic molds and thermosetting plastic molds. Steel for plastic molds requires certain properties such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance. In addition, plastic mold steel is also required to have good processabilities, such as small heat treatment deformation, good processing performance, good corrosion resistance, good grinding and polishing performance, good repair welding performance, high roughness, good thermal conductivity, and working condition size and shape stability, etc.

Plastic Mold Steel
If you want to mold injection molding or extrusion molding, you can choose hot work mold steel. If you want thermosetting forming and molds that require high wear resistance and high strength, you can choose cold work mold steel.
Mold steel is the foundation of the mold manufacturing industry. The process flow of mold steel is not completely consistent in different countries. But the same are some common steps.
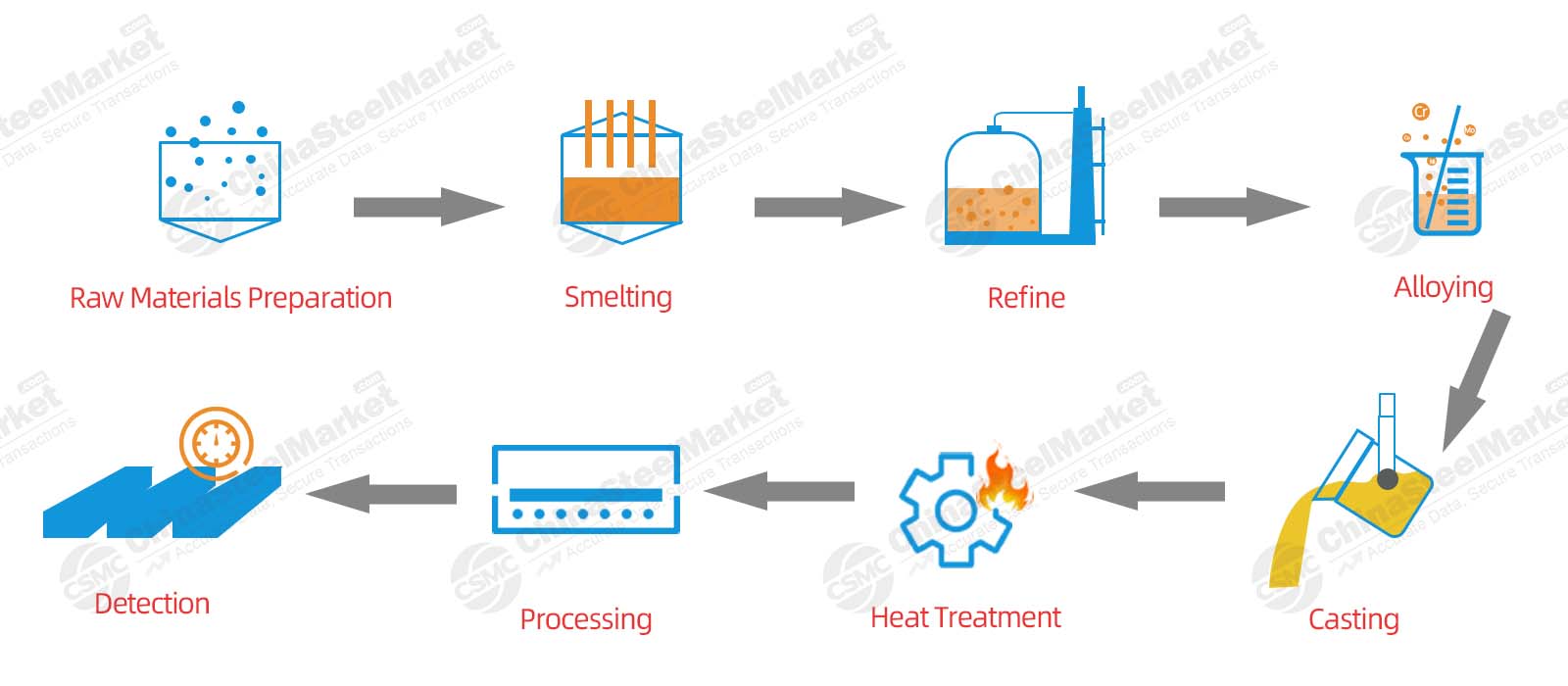
Mold Steel Process
In international trade, if customers want suitable mold steel, they must pay attention to the grade of steel. CSMC will organize the Chinese grades and international grades of mold steel and display them in the table below.
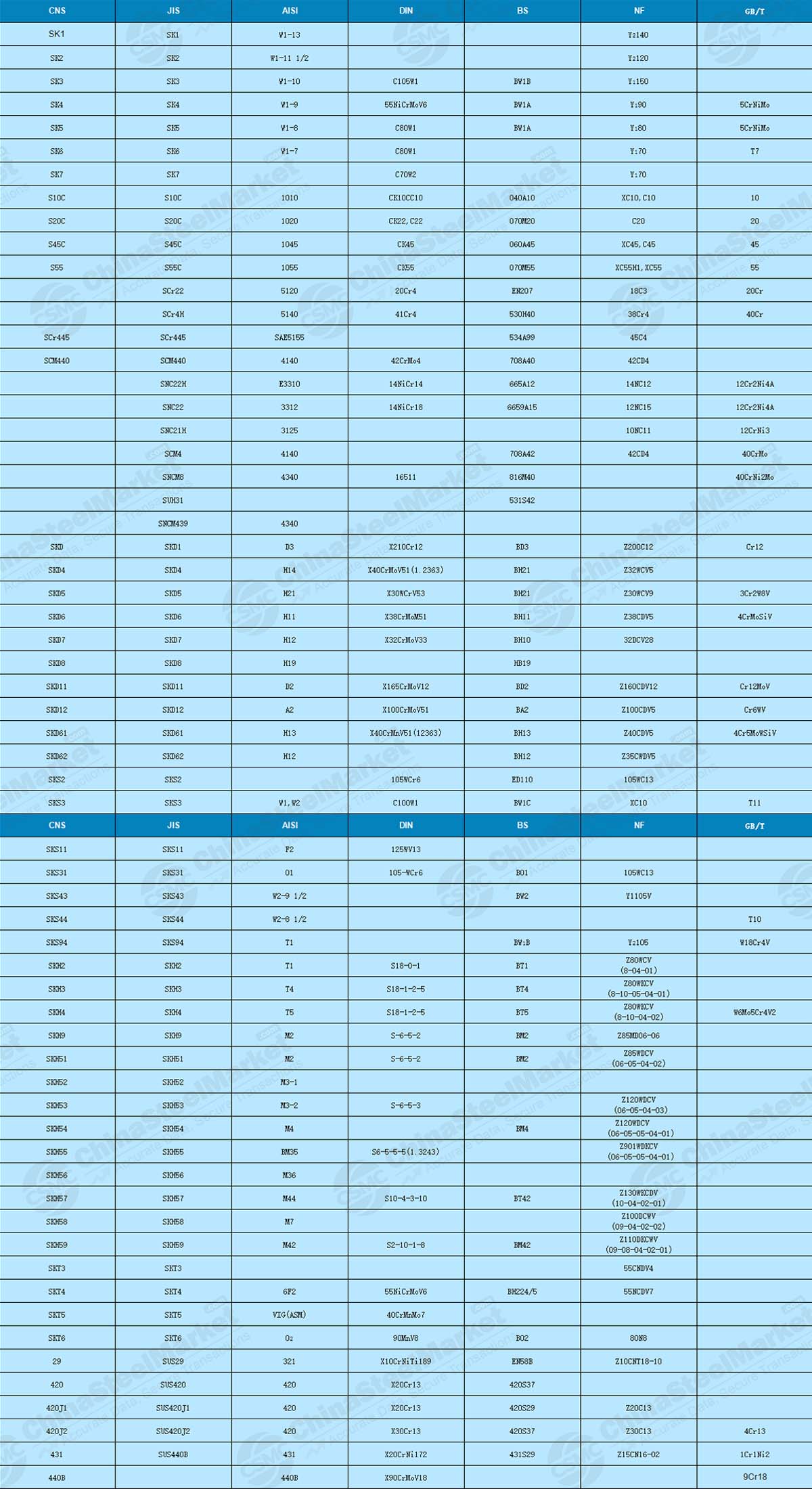
Mold Steel Grade Comparison Table
Mold steel, the head mold material, is the basis of mold manufacturing. The quality, dimensional accuracy, surface roughness, replacement speed, and product cost of many products largely depend on the mold's quality, service life, and manufacturing cycle. With the development of the mold steel industry, various countries have developed many new steel types that meet new requirements based on the original three categories of cold work mold steel, hot work mold steel, and plastic mold steel. China's mold steel output has long been among the top in the world.
If you have any corrections, please contact the editor: gianna@chinasteelmarket.com
Editor: Gianna, Hana
Mail: gianna@chinasteelmarket.com




|

|

|

|

|
| Timely Info | Independent | Platform | Multiple guarantees | Self-operated storage |
| About us | Channel | Useful tools |
|---|---|---|
| About China Steel Market | Prices | Steel Weight Calculation |
| Contact Us | Answers | Why Choose Us |
| Terms & Conditions | Inventory | |
| Privacy Policy | Help |
Hot search words: